CSO SIRIUS+
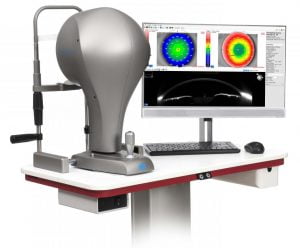
Sirius+ combines placido disk topography with Scheimpflug tomography of the anterior segment providing information on pachymetry, elevation, curvature and dioptric power of both corneal surfaces over a diameter of 12 mm. All biometric measurements of the anterior chamber are calculated using up to 100 HR corneal sections. Measurement speed reduces the effect of eye movement producing a high quality accurate measurement.
In addition to the clinical diagnosis of the anterior segment the most common uses are: refractive and cataract surgery, an IOL calculation module is available.
Objective examinations provide an accurate measurment of pupil diameter in scotopic, mesopic and photopic conditions.
Features:
- Keratoconous screening
- Glaucoma screening
- Pupillography
- IOL Calculation Module (optional)
- Intrastromal Rings
- Corneal aberrometry
CSO ANTARES
 Antares is a fully featured multi-functional corneal topographer. Antares has dedictaed software designed to help in the detection and analysis of Dry Eye. The topography function provides information about the curvature, elevation and refractive power of the cornea. It also provides many parameters to aid in the diagnosis and monitoring of the corneal surface.
Antares is a fully featured multi-functional corneal topographer. Antares has dedictaed software designed to help in the detection and analysis of Dry Eye. The topography function provides information about the curvature, elevation and refractive power of the cornea. It also provides many parameters to aid in the diagnosis and monitoring of the corneal surface.
Features:
- Corneal Topography
- Contact lens fitting with Autofit
- Advanced tear film analysis with white light (Tearscope)
- Dynamic view of non-invasive break-up time
- Blue light for fluo images
- Pupillography
- Keratoconus screening with classification
- Meibomiam Glands analysis including classification
CSO POLARIS

POLARIS is an eccessory for slit lamps, for the advanced analysis of the tear-film. It can be mounted on every brand slit lamp. It can be used throuhg the Phoenix software, or simply through the microscope.
Polaris enables interferometric examination of the lipid layer of the tear film. The biomicroscope must be focused on the tear film, while the diffused light image projected by Polaris remains out of focus. Depending on its thickness and regularity, the lipid layer may appear like any of the following: amorphous structure, marble appearance, wavy appearance, yellow, brown, blue or reddish interference fringes. The following figures show some interferometric images.
Polaris can also be used to assess the regularity of the corneal profile. By inserting the specific grids inside the internal cylinder of the instrument, a series of concentric rings is projected onto the cornea thus performing a keratoscopy. If the corneal surface is regular, the concentric rings will all be at the same distance. Any irregularities in the surface of the cornea will result in irregularities of the reflected image.